In the fast-paced world of professional services, managing team workload effectively is the key to profitability, client satisfaction, and employee well-being. Juggling multiple projects, tight deadlines, and shifting priorities can quickly lead to burnout and inefficiency, especially in growing agencies where manual reporting and timesheet fatigue are common pain points. This guide cuts through the noise, offering a curated roundup of nine powerful workload management strategies specifically tailored for mid-sized teams.
We will move beyond generic advice to provide actionable steps, real-world examples, and fresh perspectives on how to implement these methods. For agencies grappling with extensive client tasks, implementing robust marketing automation for agencies can significantly enhance efficiency and scale services without adding to the workload.
Whether you're an operations leader looking to refine project flows or a team lead aiming to overhaul your group's approach, these proven techniques will help you regain control. You will learn to enhance productivity and build a more sustainable operational rhythm. For teams leveraging calendar data, platforms like TimeTackle can be instrumental in implementing and tracking these strategies by automatically capturing activities and providing insights into where time is truly spent, ensuring your workload management efforts are data-driven and effective.
1. Time Blocking
Time blocking is a powerful workload management strategy where you meticulously plan your day by assigning specific tasks to dedicated blocks of time. Instead of working from a reactive to-do list, this method proactively turns your calendar into a detailed action plan. By allocating a finite amount of time for each activity, you prevent tasks from expanding to fill unscheduled hours, a phenomenon known as Parkinson's Law. This approach fosters deep work and ensures that high-priority projects receive the focused attention they deserve.
This method is highly effective for agencies and professional services teams juggling multiple client projects. For instance, a software development team can block out a two-hour "sprint coding" session, free from meetings or notifications, to maximize productivity. Similarly, a consultant can block 90 minutes for "client A financial modeling" and another 60 minutes for "client B report drafting," ensuring balanced progress on all fronts. This structure brings predictability to an otherwise chaotic workload.
How to Implement Time Blocking
To get started, begin by auditing your typical workday and identifying your most productive hours. Then, use these insights to build your schedule.
- Start with Larger Blocks: Begin with 60 to 90-minute blocks for significant tasks. As you become more proficient, you can break your time into smaller, more focused intervals.
- Batch Similar Tasks: Group comparable activities together. For example, dedicate a one-hour block to responding to all client emails or making all necessary phone calls to minimize context switching.
- Schedule Buffers: Add 10-15 minute buffer blocks between major tasks. Use this time to stretch, grab a coffee, or mentally transition to the next activity without falling behind schedule.
- Color-Code Your Calendar: Assign different colors to various task types (e.g., green for client work, blue for internal meetings, red for deep work) for a quick visual overview of your day. For more insights on this, you can master your schedule with advanced calendar management skills.
2. Getting Things Done (GTD)
Getting Things Done (GTD) is a comprehensive productivity methodology designed to help you manage your workload by moving ideas and tasks out of your mind and into an external system. Popularized by David Allen, its core principle is that your mind is for having ideas, not holding them. By capturing everything that has your attention, you free up mental space to focus on executing tasks, making it one of the most trusted workload management strategies.
This system is invaluable for professional services teams where countless client requests, internal projects, and administrative duties compete for attention. For example, a consulting firm can use GTD to capture every client deliverable, follow-up email, and research point into a trusted system like a project management tool. This ensures no detail is missed and allows consultants to switch contexts between clients without losing track of commitments. The structured approach brings clarity and control to a high-stakes, multi-project environment.
How to Implement GTD
Implementing GTD starts with capturing everything and then processing it through a clear workflow. The key is building trust in your external system.
- Start with a Simple Capture System: Use a digital app (like Trello or Asana) or a physical notebook to capture every single task, idea, and commitment. Don't filter at this stage; just get it all out.
- Use the 2-Minute Rule: When processing your inbox, if a task takes less than two minutes to complete, do it immediately. This prevents small, easy tasks from cluttering your to-do list.
- Focus on the Weekly Review: The "Weekly Review" is the keystone habit of GTD. Dedicate time each week to review open projects, clear your inboxes, and update your lists to ensure the system remains current and trustworthy.
- Organize by Context, Not Priority: Group tasks by the context needed to complete them (e.g., @Office, @Calls, @Computer). This makes it easy to see what you can do right now, given your location and available tools. For more on the methodology, you can visit the official Getting Things Done website.
3. Pomodoro Technique
The Pomodoro Technique is a time management method that breaks work into focused 25-minute intervals, known as "pomodoros," separated by short 5-minute breaks. Developed by Francesco Cirillo in the 1980s, this approach uses a timer to create a sense of urgency and maintain high concentration. After four consecutive pomodoros, you take a longer 15-30 minute break, which helps prevent mental fatigue and burnout. This strategy is excellent for managing a heavy workload by making large tasks feel less daunting and more approachable.
This method is particularly beneficial for roles requiring deep concentration, such as software development or content creation. A developer can dedicate one pomodoro to debugging a specific function, knowing a break is imminent. Likewise, a copywriter battling writer's block can commit to just 25 minutes of writing, making it easier to start. The built-in breaks encourage stepping away from the screen, which is crucial for maintaining focus and creativity throughout the day, making it one of the most effective workload management strategies for creative and technical teams.
How to Implement the Pomodoro Technique
Getting started is simple, as it requires little more than a timer and a commitment to honoring the intervals. The key is to protect your focus during each 25-minute sprint.
- Plan Your Pomodoros: At the start of your day or task, decide what you will work on and estimate how many pomodoros it will take. This adds a layer of planning to your execution.
- Use the Breaks Wisely: Your 5-minute breaks should be a complete mental reset. Step away from your desk, stretch, or grab a glass of water. Avoid checking emails or starting another small task.
- Adjust Interval Lengths: While the classic model is 25/5, feel free to experiment. If you find your focus lasts longer, try 50-minute work sessions with 10-minute breaks. The goal is to find a rhythm that works for you.
- Use a Dedicated Timer: Utilize a physical timer or a digital app. Many Pomodoro apps can also block distracting websites during your focus intervals, further enhancing your concentration. For more background on the method, you can explore resources from its creator at Francesco Cirillo's official site.
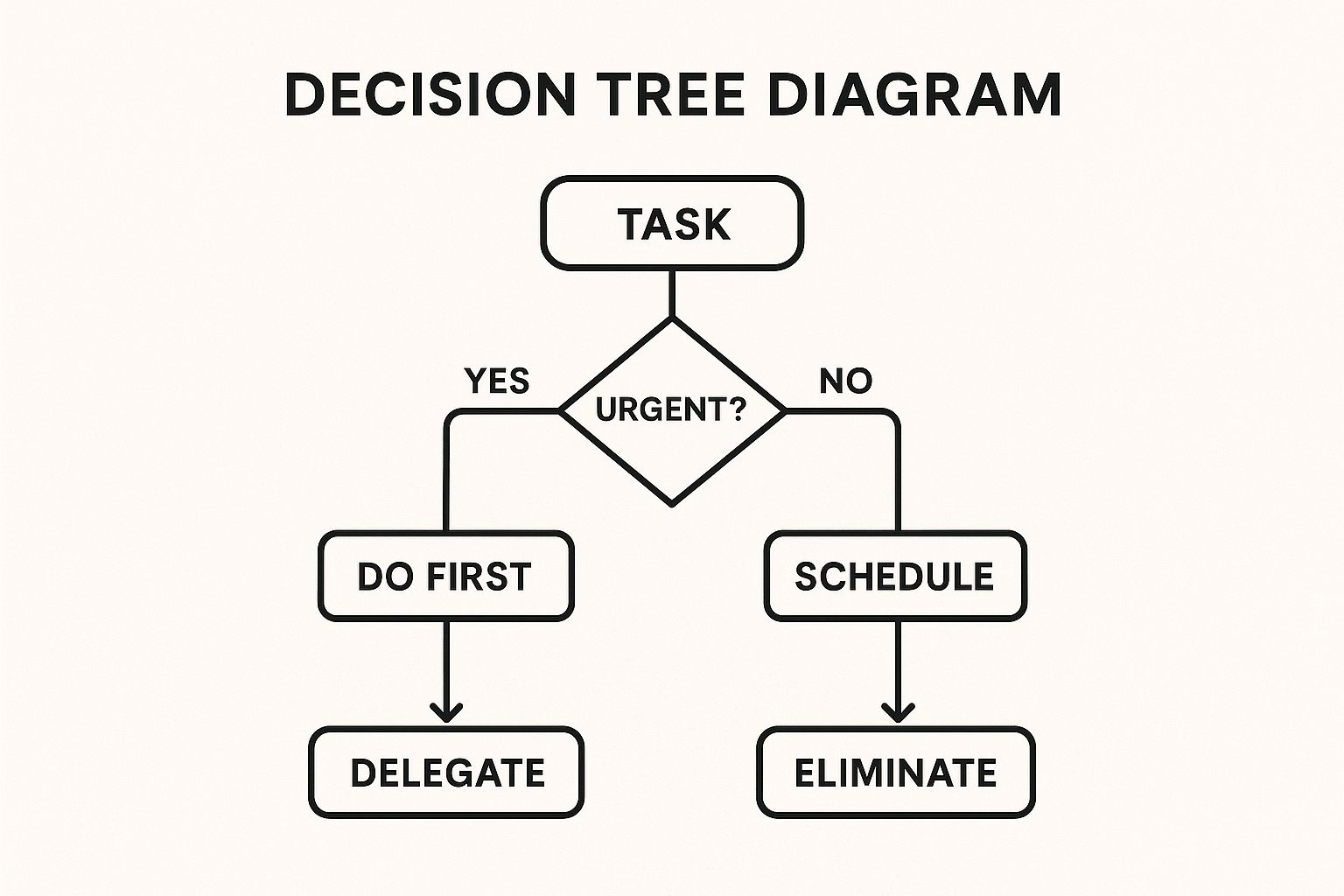
4. Eisenhower Matrix (Priority Matrix)
The Eisenhower Matrix is a classic decision-making framework that helps teams and individuals categorize tasks based on two key dimensions: urgency and importance. Rather than treating all tasks as equal, this method forces a critical evaluation of what truly requires immediate attention versus what contributes to long-term goals. By sorting tasks into four distinct quadrants, it provides a clear roadmap for action, making it one of the most effective workload management strategies for achieving focus and reducing reactive work.
This visualization illustrates the simple yet powerful decision flow of the Eisenhower Matrix, guiding you to classify any task based on its urgency and importance.
The diagram clearly separates activities into actionable categories, ensuring that effort is allocated strategically rather than just reactively. For professional services firms, a project manager can use this to prioritize feature development, distinguishing between a critical client-facing bug (Urgent & Important) and a nice-to-have internal tool update (Important, Not Urgent). This prevents the team from getting bogged down by low-impact, "loud" requests and maintains momentum on strategic objectives.
How to Implement the Eisenhower Matrix
Getting started involves honestly assessing each task against the two core criteria. This discipline helps shift focus from merely being busy to being effective.
- Define "Important" Clearly: Importance should be tied directly to your agency's or project's core goals. A task is important if it moves you significantly closer to a desired outcome, like client retention or revenue growth.
- Focus on Quadrant 2: The key to proactive workload management is spending most of your time on "Important, Not Urgent" tasks. These are activities like strategic planning, team development, and process improvement that prevent future crises.
- Be Ruthless with Quadrants 3 & 4: Actively delegate or automate "Urgent, Not Important" tasks (e.g., routine administrative requests). Eliminate activities in the "Not Urgent, Not Important" quadrant (e.g., unproductive meetings, time-wasting habits).
- Review and Reset Regularly: Your matrix is not static. Re-evaluate it daily or weekly to ensure your priorities are still aligned with shifting project demands and client needs. This keeps the framework relevant and effective.
5. Kanban Boards
Kanban is a highly visual workload management strategy that helps teams visualize their workflow, limit work-in-progress (WIP), and maximize efficiency. It uses a board with columns representing stages of a process, and cards representing individual tasks. As work progresses, cards move from left to right, providing a clear, real-time picture of what’s being worked on, what’s coming up, and where bottlenecks are forming. This transparency makes it easier to balance workloads and improve flow.
This method is ideal for teams with continuous workflows, such as creative agencies managing design requests or support teams handling client tickets. For example, a marketing agency can use a Kanban board with columns like "Backlog," "In Progress," "Client Review," and "Complete" to track campaign assets. This visual system ensures no task is overlooked and everyone on the team has visibility into the overall project status, preventing individual members from becoming overloaded.
How to Implement Kanban Boards
Getting started with Kanban is straightforward and focuses on visualizing your existing process first, then refining it over time.
- Start with Simple Columns: Begin with a basic board structure like "To Do," "Doing," and "Done." Map your current workflow to these columns and expand or adjust them as you identify more distinct stages in your process.
- Set Work-in-Progress (WIP) Limits: Assign a maximum number of tasks that can be in the "Doing" column at any given time. This crucial step prevents multitasking and highlights bottlenecks, forcing the team to resolve issues before pulling new work.
- Use Swimlanes for Categorization: Organize the board with horizontal "swimlanes" to separate different types of work, such as by client, project priority, or service type. This provides an additional layer of clarity to your workflow.
- Integrate with Your Tools: Enhance your board's power by connecting it to your project management software. You can supercharge your workflow with tools that offer robust Kanban features and explore how Asana integrations can boost productivity for your team.
6. Energy Management
Energy management is a nuanced workload management strategy that prioritizes aligning tasks with your natural energy levels, rather than just managing time. This approach acknowledges that human energy, not time, is the most valuable resource for productivity. By matching high-demand tasks with peak energy periods and scheduling routine work for low-energy troughs, you can dramatically improve output, enhance work quality, and significantly reduce the risk of burnout. This method shifts the focus from "how many hours can I work?" to "how effective can I be within those hours?"
This strategy is a game-changer for creative agencies where innovation is paramount. A design team, for example, can schedule its most intensive brainstorming and conceptual work in the late morning when cognitive function is often highest. Conversely, administrative tasks like updating project management software or responding to non-urgent emails can be reserved for the post-lunch dip. Similarly, a consultant can block their peak energy window for high-stakes client presentations, ensuring they are sharp, focused, and persuasive when it matters most.
How to Implement Energy Management
Start by becoming more aware of your personal energy rhythms. A simple audit over a week or two can reveal powerful insights into when you are most productive.
- Track Your Energy Levels: For one week, rate your energy on a scale of 1-10 every hour. Note patterns, identifying when you feel most focused and when you feel drained.
- Schedule Strategically: Align your most important and cognitively demanding tasks with your identified high-energy periods. This is your prime time for deep work.
- Utilize Low-Energy Times: Use your low-energy windows for less demanding activities like filing expenses, organizing your inbox, or planning your next day.
- Build in Recovery: Integrate short breaks or "recovery rituals" throughout the day, such as a quick walk, stretching, or a few minutes of mindfulness. For more ideas on this, explore these tips on how to manage your energy more effectively.
7. Agile/Scrum Methodology
Agile methodology is an iterative approach to workload management that prioritizes flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. Instead of planning a large project in full from the outset, Agile breaks work into smaller, manageable increments. Scrum, a popular Agile framework, organizes these increments into time-boxed iterations called sprints, typically lasting one to four weeks. This structure allows teams to adapt to changing client needs and deliver value consistently.
This framework is exceptionally powerful for professional services teams where project scope can evolve. For instance, a marketing agency can use a two-week sprint to launch a specific digital ad campaign, test its performance, and then use the findings to plan the next sprint. Similarly, a consulting firm can deliver a financial model in one sprint and a market analysis report in the next, allowing the client to provide feedback at each stage. This iterative cycle is one of the most dynamic workload management strategies for maintaining momentum and alignment.
How to Implement Agile/Scrum Methodology
Adopting Agile requires a shift in mindset towards collaboration and iterative progress. Start small and focus on the core principles to build momentum.
- Start with a Pilot Team: Before an organization-wide rollout, test the Scrum framework with a single, receptive team. Use their experience to refine your process and create a model for success.
- Invest in a Scrum Master: A dedicated and well-trained Scrum Master is crucial. This person facilitates the process, removes obstacles for the team, and ensures Agile principles are followed.
- Prioritize Deliverables: The goal of each sprint is to produce a "working increment" of value. Focus on completing tangible deliverables rather than just being busy with tasks.
- Embrace Retrospectives: The sprint retrospective is a vital meeting where the team discusses what went well and what could be improved. Make this a non-negotiable ceremony to foster a culture of continuous improvement. You can learn more about these core principles from resources like the Agile Alliance.
8. Batch Processing
Batch processing is a workload management strategy that groups similar tasks together to be completed in a single, dedicated time block. Instead of constantly shifting mental gears between different types of activities, this method minimizes context switching. By focusing on one kind of work at a time, you reduce the mental "setup" time required for each new task, which boosts efficiency and conserves cognitive energy. This principle, popularized in books like Tim Ferriss's The 4-Hour Work Week, borrows from efficient manufacturing processes to streamline knowledge work.
This approach is invaluable for creative and marketing agencies looking to maximize output. For instance, a social media manager could dedicate a two-hour block on Monday to create and schedule all social media content for the entire week. Similarly, a finance consultant might batch all their invoicing and expense reporting into a single block on Friday afternoon. This ensures these essential but often disruptive tasks are handled efficiently without fragmenting the focused time needed for high-value client work.
How to Implement Batch Processing
Getting started involves identifying recurring, similar tasks that can be bundled. The goal is to create a rhythm where your brain can stay in a single mode of operation for an extended period.
- Identify Batchable Tasks: Look for activities that are repetitive or require a similar mindset. Good candidates include responding to emails, making client follow-up calls, creating graphics, or processing administrative paperwork.
- Schedule Dedicated Batches: Just like with time blocking, assign specific times in your calendar for these batches. For example, set aside 30 minutes at 11:30 AM and 4:00 PM each day solely for checking and replying to emails.
- Prepare Your Resources: Before starting a batch, gather all necessary tools, information, and resources. If you're batching client reports, have all the data, templates, and contact information ready to go.
- Use Templates and Automation: Accelerate repetitive work within your batches by using templates for emails, reports, or proposals. This further reduces the cognitive load and time spent on each individual item in the batch.
9. OKRs (Objectives and Key Results)
OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) is a goal-setting framework that serves as one of the most powerful workload management strategies for aligning teams and focusing efforts. The system connects ambitious, qualitative Objectives with specific, measurable Key Results that track progress. This structure clarifies what needs to be achieved (the Objective) while defining how success will be measured (the Key Results), ensuring everyone moves in the same strategic direction.
This framework is highly effective for agencies aiming to scale, as it shifts the focus from simply being busy to achieving tangible, impactful outcomes. For example, a marketing agency might set an Objective to "Become the leading content provider in the fintech space." The corresponding Key Results could be: "Increase organic blog traffic by 40%," "Secure 15 high-authority backlinks," and "Generate 100 new MQLs from content downloads this quarter." This aligns the workload of content creators, SEO specialists, and demand generation teams toward a single, unified goal.
How to Implement OKRs
To successfully integrate OKRs, start by defining a clear vision for a specific period, typically a quarter. From there, build your framework with focused, measurable targets.
- Limit Your Focus: Begin with no more than 3-5 high-level objectives per team or department for each cycle. Spreading focus too thin dilutes impact and makes tracking cumbersome.
- Make Key Results Quantifiable: Each Key Result must be a specific, measurable metric. Avoid vague outcomes; instead of "Improve client satisfaction," use "Achieve an average Net Promoter Score (NPS) of 9.2 across all accounts."
- Conduct Regular Check-Ins: Schedule weekly or bi-weekly check-ins to review progress. These meetings are crucial for identifying roadblocks, re-prioritizing tasks, and keeping the team motivated and aligned.
- Decouple from Compensation: OKRs are designed to encourage ambitious "stretch" goals. Tying them directly to performance reviews or bonuses can lead to sandbagging, where teams set easily achievable targets to guarantee success. As John Doerr highlights in his book Measure What Matters, a 70% achievement rate on a difficult goal is often a sign of healthy ambition.
Workload Management Strategies Comparison
| Methodology | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Blocking | Moderate – requires initial setup and discipline | Digital calendars/tools needed | Better focus, reduced multitasking, realistic workload | Routine scheduling, individual productivity, deep work | Reduces decision fatigue, clear work-life boundaries |
| Getting Things Done (GTD) | High – complex setup and ongoing maintenance | Task management apps, consistent reviews | Mental clarity, scalable task management, stress reduction | Comprehensive life/task organization, large task loads | Externalizes tasks, focuses on actionable next steps |
| Pomodoro Technique | Low – simple timer-based method | Timer or apps | Increased focus, reduced burnout, measurable sessions | Focused work sprints, overcoming procrastination | Prevents burnout, improves concentration |
| Eisenhower Matrix | Low – simple to understand and apply | Minimal (pen/paper or apps) | Clear priority setting, reduced busy work | Prioritizing daily tasks, decision-making under pressure | Identifies important vs urgent work, easy implementation |
| Kanban Boards | Moderate – requires maintenance and discipline | Kanban tools or physical boards | Workflow transparency, bottleneck identification | Team projects, workflow management, visual task tracking | Provides clear visibility, encourages continuous improvement |
| Energy Management | Moderate – requires self-tracking and adjustments | Self-monitoring tools, flexible schedule | Improved productivity by aligning tasks with energy | High variability workflows, optimizing personal productivity | Reduces burnout, leverages natural productivity peaks |
| Agile/Scrum Methodology | High – cultural change, team training needed | Collaboration tools, dedicated roles | Flexibility, continuous delivery, strong teamwork | Software dev, iterative projects, cross-functional teams | Adaptable to change, promotes collaboration |
| Batch Processing | Low to moderate – simple batching concept | Suitable workspace/tools for batching | Increased efficiency, reduced context switching | Repetitive or similar task execution, admin work | Minimizes task switching, builds momentum |
| OKRs (Objectives and Key Results) | High – considerable planning and follow-up | Goal tracking tools, team alignment | Clear alignment, measurable progress, ambitious goals | Organizational focus, quarterly/annual goal setting | Aligns teams, drives stretch performance |
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Agency's Success
We've explored nine distinct and powerful workload management strategies, from the focused sprints of the Pomodoro Technique to the high-level goal alignment of OKRs. The central takeaway isn't that one single method is superior to all others. Instead, the path to sustainable productivity for your agency lies in building a customized, hybrid system that reflects your team's unique culture, client demands, and project complexities.
The true art of workload management is about moving beyond theory and into active, intentional practice. The most successful professional services teams don't just pick a strategy and stick with it indefinitely. They experiment, iterate, and adapt, creating a flexible toolkit that can be deployed as circumstances change. This iterative approach is what transforms a good agency into a great one, capable of delivering exceptional work without succumbing to burnout.
Building Your Agency's Custom Toolkit
Think of the strategies in this article not as rigid rulebooks, but as ingredients. Your goal is to combine them to create a recipe that works for your specific team. For example:
- For Creative Teams: You might combine the visual workflow of Kanban Boards with the focused bursts of the Pomodoro Technique to manage multiple client projects while protecting deep work time.
- For Consulting Teams: You could use the Eisenhower Matrix for daily task prioritization and align those tasks with quarterly OKRs to ensure every billable hour contributes to strategic goals.
- For Operations Teams: Batch Processing for administrative tasks like invoicing and reporting, combined with a team-wide GTD system, can create significant efficiency gains and reduce mental clutter.
The key is to encourage your team to try different combinations and provide feedback. What reduces friction? What enhances focus? Which approach brings the most clarity to complex projects?
From Strategy to System: The Role of Technology
Implementing these strategies effectively often requires the right operational backbone. While manual tracking can work initially, it quickly becomes a bottleneck, creating the very administrative overhead you’re trying to eliminate. This is where technology plays a crucial role. Modern platforms can automate the tracking and analysis, giving you the data needed to refine your approach.
To truly optimize your chosen workload management strategies, you need visibility into how time is actually spent. Integrating the right software turns abstract goals into measurable outcomes. For agencies ready to scale their operations, exploring the best workflow management tools can provide the necessary structure to support these dynamic methods, ensuring your processes are as efficient as your people.
By moving from a reactive, "fire-fighting" mode to a proactive, strategic approach, you empower your team to do their best work. This isn't just about getting more done; it's about creating a sustainable environment where top talent can thrive, client satisfaction soars, and your agency achieves predictable, profitable growth. The journey starts with a single step: choosing one or two strategies to test, measure, and refine.
Ready to replace guesswork with data? TimeTackle provides automated time tracking and analytics from your team's calendar data, giving you the objective insights needed to balance workloads, improve utilization, and see which management strategies truly work. Discover your team’s real capacity and build a more productive, sustainable future with TimeTackle.